The ingredients of cement, as well as its properties and functions, are critical for maintaining the cement’s quality in construction. An essential component of the construction is cement, which functions as a binding agent. Almost every construction project necessitates the use of cement. Ordinary Portland cement is made up of various ingredients in varying proportions. Each ingredient gives the cement a unique property. To produce high-quality cement, we must understand the proportions, functions, and limitations of the various ingredients of cement.
Cement is one of the most significant structural materials used in building. When cement is mixed with aggregates and sand, it becomes concrete, and when cement is mixed with sand, it becomes mortar, which is used for brickwork, plastering, and flooring, among other things. This article is about the ingredients of cement and properties of cement.
Ingredients of Cement
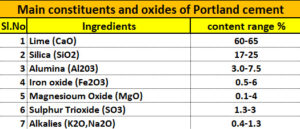
Cement is manufactured from Lime, silica, alumina and iron oxide. Lime is obtained from limestone and silica oxides; alumina and iron are found in clay and shale. Major ingredients of cement is as follows
- Lime
- Silica
- Alumina
- Iron oxide
- Magnesium oxide
- Sulphur trioxide
Table showing major Ingredients of Cement and content pecentage
Lime – Major Ingredients of Cement
Lime is the main ingredient of cement, accounting for 60-65% of total cement weight. This is the main ingredient used in the production of calcium silicates and aluminates, mostly responsible for the cementing properties and strength. In addition to the above, the proportion of lime in cement changes its properties. A lower lime content can reduce cement strength, while a higher lime content can render the cement unsound. For the required strength of concrete, the correct proportions of lime are required.
Silica – Second Major Ingredient of cement
SiO2 or silicon dioxide is called silica. Generally, silica is responsible for the formation of dicalcium silicate and tricalcium silicate by reacting with lime. However, correct proportions of silica play a major part in inducing cement strength.
Alumina
Alumina is responsible for lowering the clinkering temperature and controlling the setting time of cement which in turn can imparts quick setting properties in cement. Likewise, any increase in alumina content will weaken the cement.
Iron oxide
Iron oxide is responsible for the colour of the cement and it acts as a flux in the cement manufacturing process. Generally it acts as a flux in high temperatures and combines with calcium and alumina to form tricalcium alumino ferrite which is the main ingredient behind the hardness of cement.
Magnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide is found in minor traces but increase in the quantity can reduce the strength of cement.
Sulphur Trioxide
Sulphur trioxide is available in traces but any increase can affect the cement quality.
PROPERTIES OF CEMENT
Cement is the most important structural material used in construction. Moreover, it is the most popular binding material and can be used in a wide range of structures, from houses to skyscrapers, industrial structures, bridges, and roads. Cement, when combined with sand and aggregates, forms concrete; when combined with sand, it forms mortar. Accordingly, the serviceability, strength, and durability of a structure are solely determined by the quality of cement used in concrete and mortar. Cement properties are directly related to the proportioning of ingredients, grinding, packing, and so on.




2 comments
Comments are closed.