Components of dams play specific roles in maintaining the primary responsibility of water management. Basically,dams are barriers built across water bodies to regulate water flow and levels. Furthermore, dams are required for everything from simple water supply and irrigation projects to large hydropower generation plants and disaster control projects. The components of dams and their functions are the topic of this article.
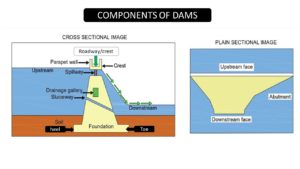
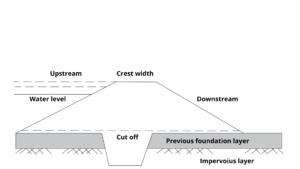
Basically, the part of a dam where the water is collected is known as the upstream side. Generally, the water level is high on the upstream side. Likewise, the downstream are the dam parts with low water levels.
Components of Dams
A dam construction generally includes a water-retaining structure (the dam), a water-releasing structure (the spillway), a water-conveying structure (conduits), and other components (such as power plants). Dam components play an important role in maintaining primary responsibility of water management.
- Water-retaining structure
- Water-releasing structure
- Water conveying structure
Related posts from vincivil world
Components of Dams – You tube video
Water-retaining structure – Components of Dams
The water-retaining structure is the dam’s walled structure that resists water while allowing a controlled amount to flow downstream. Accordingly, the side of the barrier where water is collected is known as the upstream side, and where the water flows is known as the downstream side. Generally, the following component of dams makes up the dam’s water-retention section.
- Heel
- Toe
- Abutment
- Crest
- Cutoff
- Parapet wall
Heel
Generally, the part of the dams meeting with the groundwater or upstream side is called the heel. (Ref fig.)
Toe
Basically, The portion of the dams meeting with the groundwater or downstream side is called the Toe.(Ref fig)
Abutment
An abutment is the valley sides of the dams constructed with concrete or masonry work. Accordingly, the abutments’ purpose is to support the dam’s wall. Moreover,abutments support the lateral pressure.
Crest/Roadway of Dams
The section of the dams used as a roadway or walkway is the crest. It is the upper area of the dam.
Parapet wall
Generally, the parapet wall is seen below the crest near the roadway. Similarly, this assists in the dam investigation and safety barriers.
Water-releasing structure: Components of dams
Mainly, the components of dams that allow water to flow downstream are known as the water-releasing structure. Generally, these dam components are technically known as the dam’s spillways. Generally, the spillway’s mechanism allows for controlled water volume. A spillway contains the following components.
- Galleries
- Spillways
- Diversion tunnel
- Sluiceway
- Freeboard
- Conduit
Galleries – Components of dams
Generally, galleries are hollow openings passing through the dam as shown in fig. However, the main purpose of providing a drainage gallery is to collect seepage water from the foundation and body of the dam and drain it out. In this case, the seepage water received by foundation galleries is drained away under gravity. Accordingly, the galleries are broadly divided into …
- Grouting gallery
- Inspection Gallery
- Drainage gallery
- Valve gallery
- Transformer Gallery


Diversion tunnel
The purpose of the diversion canal is to redirect the water. Diversion tunnels are constructed during the construction stage of dams.
A diversion tunnel may also be constructed to divert floodwater to divert water from mountainous regions to low-lying areas experiencing a water shortage supply.
Cut off
A Cut off is an impervious barrier constructed beneath the earthen dams. Generally, the main function is to reduce the loss of stored water in the reservoir by preventing seepage.
Spillway- Components of dams
Basically, the role of the spillway is to convey excess water and prevent damage. In this case, the water passes from tupstream to downstream. Moreover, the spillway helps in the emergency discharge of water.
They are two varieties
- Controlled spillway
- Uncontrolled spillway
However, In a controlled spillway the flood flow is regulated by the gate.
Sluice way – Components of dams
Mainly, the role of the sluiceway is to remove the silt accumulated.
Freeboard
Basically, free board is the interval between the dam heads to the maximum water level on the upstream side.
Water conveying structure – Components of dams
Water conveying structure is mainly conduits and convey the water from reservoirs through, around, or under an embankment dam
Conduit – Components of dams in water conveying
Basically, Conduits are closed pipe structures. Generally, conduits act as a passage for the water supply. Accordingly, bottom discharge conduits are pipes that cross the body of the dam from the upstream to the downstream sides enabling water flow.
Examples of some major dams
Bhakra Dam ( Gravity dam )
The Bhakra Dam is an Indian gravity dam built in Himachal Pradesh across the Sutlej River. This dam was built in 1963. The dam stands 226 metres tall. The dam measures 518 metres in length. This dam’s reservoir is known as Gobind Sagar. The Bhakra Dam is made up of layers of light red clays and sandstone. Basically, there are four spillways on this dam. Similarly, this dam aids in irrigation, hydroelectric power generation, and recreational activities. Obviously, this dam is a major source of irrigation water supply in Haryana, Punjab, and Rajasthan.
Idukki dam ( Arch dam )
The Idukki dam in Kerala is an arch dam built across the Periyar river. The height is 554 feet. One of Asia’s largest arch dams. Generally, The dam generates hydroelectricity, serves as an irrigation system, and serves as a tourist attraction. Significantly, It is situated between the Kuravan and Kurathi hills.
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam (Masonry Dam)
Nagarjuna Sagar Dam is a stone masonry dam completed in 1967. The dam is a symbol of modern architecture. The purpose of this project was to generate hydroelectricity. It has a 26-crest gate.
The Hirakud Dam (Earthern dam)
The Hirakud dam is located in Orissa, near Sambalpur, on the Mahanadi River. The dam is 4800 metres long and 59 metres high. Completed in 1957, it is the oldest multipurpose dam. The Hirakud Dam is 4800 metres long and 59 metres high. The dam’s total storage capacity is 1841 million cum.
KARIBA DAM (Double curvature arch dam)
Kariba Dam is a double curvature arch dam constructed in 1960. It has been built over the Zambezi river. The crest length is 620m and 128m high. The dam provides an example of improving the quality of rocks.



One comment
Comments are closed.