Destructive Tests (DT) on Hardened Concrete are essential for understanding how concrete behaves under extreme stress. Unlike non-destructive methods, these tests deliberately break or damage the material to measure its ultimate strength and durability. The most common destructive tests on concrete include compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, and flexural strength tests. These tests help engineers assess the quality of hardened concrete, ensuring it meets structural and safety requirements. In this article, we will dive into the types of destructive concrete tests. We will explore their significance in construction. Testing hardened concrete is critical for long-term performance and safety.
Destructive tests (DT) and Non-destructive tests (DT) are the tests done on hardened concrete. Concrete is the oldest and most important construction material in the world. Testing of the concrete plays an important role to know the strength, durability and condition of the structure. This article is about the types of Destructive and non-destructive tests done on concrete.
Table of contents
Types of tests for Hardened Concrete
Types of tests for hardened concrete include Non-Destructive Tests (NDT) and Destructive Tests (DT). Non Destructive Testing methods evaluate concrete integrity without damage, using techniques like ultrasonic testing and rebound hammer tests. In contrast, Destructive Testing involves breaking concrete samples to assess properties like compressive strength, tensile strength, and flexural strength. These tests are crucial for ensuring structural safety and performance .
Tests on hardened concrete are classified into two types.
- Non destructive tests (NDT)
- Destructive tests (DT)
In this article we will discuss about destructive tests on Concrete
Destructive tests on Hardened Concrete
The quality of concrete is important for construction. Hardened concrete attains strength as it matures. The destructive test of concrete helps to understand the behavior and quality by breaking the test specimen at certain loads. The primary step of the destructive test is to cast test specimens from freshly made concrete.
The destructive testing method is suitable and economically beneficial for the concrete specimens that are produced at a large scale. The main intention of destructive tests is to investigate the service life. They also aim to detect the weaknesses of design that might not show under normal working conditions. It includes methods where the concrete specimen is broken so as to determine mechanical properties i.e. hardness and strength. This type of testing is very easy to carry out, easier to interpret, and yields more information.
Also read : Concrete mixing – Types and objectives
Significance of Destructive tests on hardened Concrete
Concrete is a basic construction material, So it should be capable to withstand heavy loads. The concrete test results mainly depend on the cement strength, water-cement ratio, concrete quality etc. The significance of destructive tests on hardened concrete lies in their ability to determine the material’s true performance under stress. These tests help assess the quality of concrete structures. They also evaluate durability and safety. Destructive concrete testing provides essential data, ensuring that concrete meets design and safety standards in construction. The main objectives of the hardened concrete test are as follows.
- Quality control
- Acceptance of concrete
- Evaluation of curing
- To provide information on the use of sand and aggregate.
- For evaluating the uniformity of concrete
- Estimates the concrete quality with standard requirements.
- To determine the uniform stress distribution.
- Investigating the behavior of concrete.
- For determining the in-place concrete strength.
- Age of concrete, etc.

Types of Destructive tests for hardened concrete
- Compressive strength test
- Splitting tensile strength test
- Flexural strength test
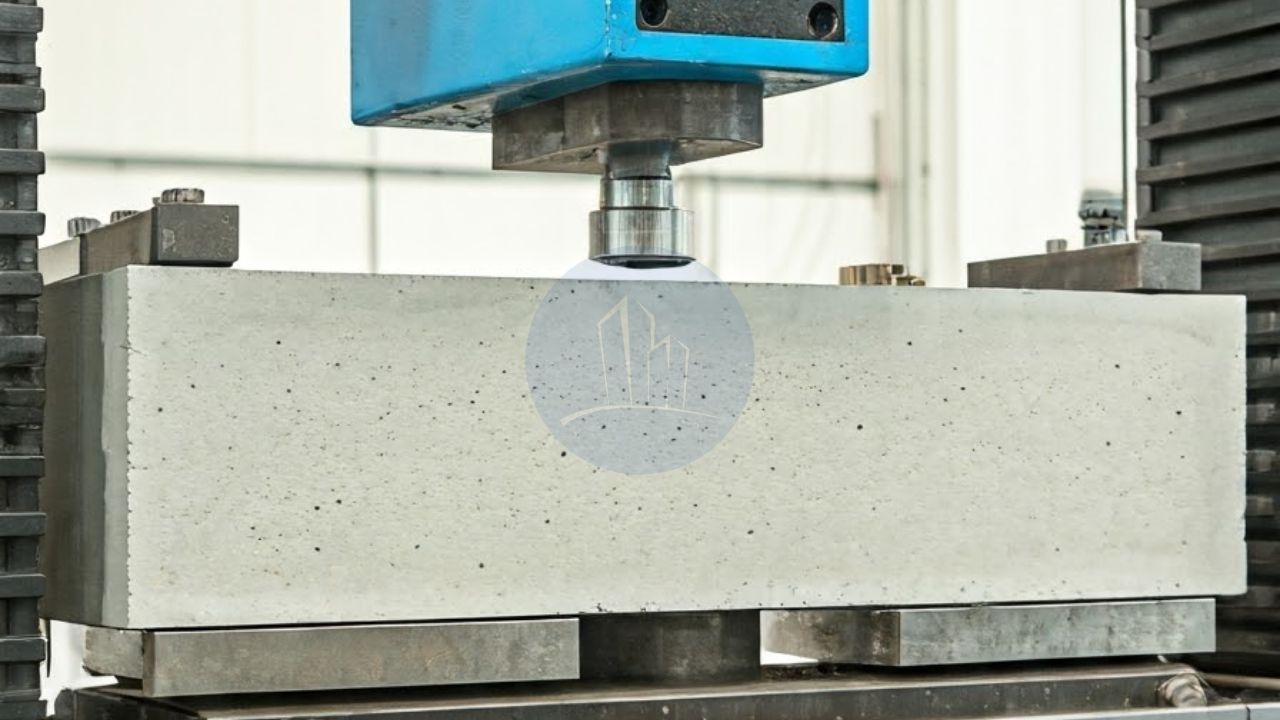
Compressive strength test of hardened concrete
The compressive strength test of hardened concrete is a crucial destructive concrete testing method. It measures the ability of concrete to withstand compressive loads without failure. In this test, cylindrical or cubic specimens are subjected to increasing pressure until they break. This testing of hardened concrete helps determine the concrete’s load-bearing capacity, ensuring structural integrity and compliance with safety standards. Compressive strength is a key performance indicator in construction quality control.
The apparatus for performing this test is a Compression testing machine. The compressive strength test of concrete is governed by several standards in different regions. Relevant codes include:
ASTM Standard: ASTM C39/C39M – “Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens” is the American standard used globally for compressive strength tests.
These codes ensure uniform procedures and accurate results in concrete testing.
Compressive strength of the concrete = Load at which the concrete breaks / Cross-sectional area of the specimen
The unit of compressive strength of concrete is N/mm^2. The test should be done at 7, 14 & 28 days.
Also Read : Compressive strength of concrete -significance and test procedure
Splitting tensile strength test
The splitting tensile strength test is a widely used method to evaluate the tensile strength of hardened concrete. Concrete is a durable construction material. Under tension, concrete is brittle in nature. Therefore it causes cracks and deteriorates. In this test, a cylindrical concrete specimen is placed horizontally and loaded along its length until it fails due to tensile stress. For this test, we use cylindrical specimens with 150 mm diameter and 300 mm height. This test indirectly measures tensile strength, offering valuable insight into the material’s behavior under tension.
Relevant codes for the splitting tensile strength test include:
- Indian Standard (IS): IS 5816:1999 – “Splitting Tensile Strength of Concrete – Method of Test.”
- European Standard (EN): EN 12390-6 – “Testing Hardened Concrete – Tensile Splitting Strength of Test Specimens.”
- ASTM Standard: ASTM C496/C496M – “Standard Test Method for Splitting Tensile Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens.”
These standards ensure consistent testing procedures for accurate results.
The tensile strength of concrete is
Splitting tensile strength of concrete, T= 2P/ Ω LD
The unit of tensile strength is N/mm. The IS 5816: 1999, ASTM C496 gives the standard aspects for this test.
Also Read : Splitting tensile strength test on concrete- Significance and test procedure
Flexural strength test
The flexural strength test evaluates the tensile strength of concrete by measuring its resistance to bending. This test is crucial in assessing how concrete performs in structures like beams, slabs, and pavements that are subject to bending forces. A beam specimen is placed on supports and loaded at the center or third points until it breaks. This provides insight into concrete’s ability to resist tensile stress.
Relevant codes for the flexural strength test include:
- Indian Standard (IS):
- IS 516:1959 – “Method of Tests for Strength of Concrete” outlines the procedure for conducting the flexural strength test.
- ASTM Standard:
- ASTM C78/C78M – “Standard Test Method for Flexural Strength of Concrete” using simple beam with third-point loading.
- European Standard (EN):
- EN 12390-5 – “Testing Hardened Concrete – Flexural Strength of Test Specimens.”
These standards guide testers to conduct the test accurately, providing reliable data on concrete’s flexural capacity
The flexural strength test and splitting tensile strength test are almost the same. Because both the tests measure the tensile strength of concrete. The flexural strength test of concrete measures the tensile strength of concrete through an indirect method.The modulus of rupture is the measure of tensile strength. Its unit is MPa or psi.
Modulus of rupture, MR = 3PL/ 2bd^2
Where,
You measure P as the ultimate applied load. L is the span length. You measure b and d as the average width and depth of the specimen at the point of fracture.
Key Takeaways
- Destructive Tests (DT) evaluate the strength and durability of hardened concrete under extreme stress.
- Common Destructive Tests methods include compressive strength, splitting tensile strength, and flexural strength tests.
- These tests assess the quality, durability, and safety of concrete structures.
- Destructive Tests helps detect design weaknesses that may not manifest under normal conditions.
- The compressive strength test measures load-bearing capacity by subjecting specimens to pressure until failure.
- The splitting tensile strength test evaluates tensile strength by loading cylindrical specimens until they crack.
- The flexural strength test measures resistance to bending, crucial for structures under tensile stress.
- Accurate testing procedures are governed by international standards such as IS, ASTM, and EN.
Conclusion
Destructive tests on hardened concrete play a vital role in ensuring structural integrity and safety in construction. By assessing the compressive, tensile, and flexural strengths, engineers can gather crucial data about the material’s performance under stress. These tests help in quality control and acceptance of concrete. They also aid in evaluating curing processes and ensuring uniformity in material properties. Adhering to established testing standards assures reliable results. It enhances the longevity of concrete structures. Ultimately, the significance of destructive testing cannot be overstated. It is essential for effective design and construction practices. Destructive testing safeguards public safety and optimizes material use.






reference infomation about the destructive and non destructive concrete test