Non destructive testing of hardened concrete plays a vital role in assessing the condition and performance of concrete structures without causing damage. Engineers use non destructive test for concrete structures to evaluate strength, durability, and uniformity while the structure remains fully functional. These NDT methods for concrete evaluation help detect cracks, voids, honeycombs, and other hidden defects that may affect long-term performance. By applying advanced hardened concrete testing techniques, professionals can estimate compressive strength, identify deterioration, and monitor the health of aging infrastructure. Modern tools like rebound hammer and ultrasonic pulse velocity support concrete strength testing without damage, making the process faster and more cost-efficient. The key advantages of NDT in concrete testing include safety, accuracy, rapid inspections, and extended service life of structures. Overall, NDT ensures reliable decision-making for repairs, rehabilitation, and quality control in construction.
Non-destructive test (NDT) and destructive tests (DT) are the the tests done one hardened concrete. Concrete is the oldest and most important construction material in the world. Testing of the concrete plays and important role to know about the strength, durability and condition of the structure. This article is about the types of Destructive and non destructive tests done on concrete.
Table of contents
Types of Concrete Tests
Concrete testing plays a vital role in determining the strength, durability, and performance of concrete structures. Engineers conduct different tests to verify that the concrete mix meets design requirements and performs safely throughout its service life. These types of concrete tests help assess important properties such as workability, compressive strength, density, and internal defects. The tests are categorized into destructive tests and non destructive tests, depending on whether the specimen is damaged during inspection. Both testing methods are essential for ensuring quality control, structural integrity, and long-term durability of concrete in construction projects. By using the right concrete testing techniques, engineers can make reliable decisions in design, repair, and maintenance works.
Concrete tests are classified into two types.
- Destructive tests (DT)
- Non – Destructive tests (NDT)
Destructive Tests
- Compressive Strength Test
- Flexural Strength Test
- Split Tensile Strength Test
- Pull-out Test
- Core Cutting and Testing
Non Destructive Tests (NDT)
- Impact Echo / Pulse Echo Test
- Rebound Hammer Test
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV) Test
- Half-Cell Potential Method
- Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Cover Meter Survey
- Schmidt Hammer Test
In this article we describes about the Non destructive testing techniques conducted on hardened concrete.
Non- Destructive testing techniques on hardened concrete
The standard method of non destructive testing of hardened concrete is carried out by testing the concrete specimens cast simultaneously with structural concrete. These destructive tests on concrete can determine the compressive, flexural, and tensile strengths. The major disadvantage of these destructive concrete testing methods is the non availability of immediate results. Moreover, the properties of the concrete specimen may differ from what it is in the actual structure. This difference is due to pouring conditions, curing factor, compaction and concrete density, etc. These tests come under the category of destructive tests (DT). Destructive testing of concrete destroys or changes the part in some way such that even if it passes the test it is no longer fit for service.
Non Destructive Test (NDT) is for determining compressive strength and other properties of concrete from existing structures or buildings. NDT testing of concrete does not destroy or change the part such that it is still fit for service if it passes the test. The non-destructive test determines the properties of concrete or structures without their destruction. Moreover, we can study its changes over time, The measurements are repeated many times and validate in detail, and gets immediate results. These NDT concrete testing methods help assess quality, strength, and durability in a quick and reliable way.
Objectives/advantages of Non destructive testing (NDT)
Non-destructive testing (NDT) helps evaluate hardened concrete structures without causing damage. It allows engineers to assess concrete strength, durability, reinforcement condition, cracks, and internal defects while the structure remains fit for service. The advantages of NDT include quick results, safety, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to monitor structures throughout their life cycle. These advantages of NDT make it widely preferred for quality assurance and structural health monitoring.
- Quality check of the existing structure.
- For determining the homogeneity, internal and external characteristics of the concrete.
- To detect the cracks and voids of the concrete structures.
- Assess the quality of concrete with the standard requirement.
- To study the ageing of concrete.
- For finding the compressive strength of structures.
- Evaluation of elastic modulus
Classification of Non-Destructive test
Hardened Concrete testing techniques/ Non Destructive testing are as follows
- Windsor Probe Test
- Rebound Hammer Test
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
- Half-Cell Potential Test
- Covermeter / Rebar Locator Test
- Impact Echo Test
Penetration Resistance Test / Windsor Probe Test
The penetration resistance test is an NDT that determines the relative strength of the concrete structures. The Windsor probe is the equipment for conducting this test. This equipment includes of powder-actuates driver or gun, probes, loaded cartridges and a gauge that measures the penetration.
The penetration depth indicates the compressive strength of the concrete. However, this depends on the aggregate type and size. This test evaluates the poor quality and deterioration of concrete
The major disadvantage of this test is getting variable results. Several probes are often shot to achieve a solid average depth for arriving a final conclusion. So we cannot determine the exact strength. But it is a quick method to evaluate the quality and maturity of concrete. Care should be taken to calibrate the instrument before taking readings.
Rebound Hammer Test
The rebound hammer is also known as Schmidt’s Hammer test. It determines the strength of concrete based on the hardness of the concrete surface. It is a surface hardness tester. The equipment consists of a spring-controlled plunger, a hammer that weighs 1.8 kg, and a graduated scale. By pressing the hammer on the concrete surface, the graduate scale measures the rebound number. A low rebound number means the concrete has low compressive strength and stiffness.
An accuracy of 15 to 20% is possible through this test. It is a simple and quick method. Also, the result relies on the surface smoothness, water content, type and size of aggregate and carbonation of the surface.
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test
Ultrasonic pulse velocity test is another type of Non-destructive test. This test measures the time of travel of ultrasonic pulse waves for evaluating the concrete quality. The UPV test units consists of a pulse generator and pulse receiver. The frequency of the wave is 50-55 kHz. The pulse generator produces the pulses and is allowed to pass through the concrete. Then we calculate the velocity, by measuring the traversing distance and the time. Higher velocity means the concrete has a higher elastic modulus and density. It also determines the cracks and flaws in the structure. Large differences in pulse velocity values indicates a defective and deteriorated concrete.
For more details : Ultrasonic pulse velocity test || UPV Test – Methods and procedure
Half-Cell Potential Test – Detecting Corrosion
The Half-Cell Potential Test is a widely used non-destructive testing (NDT) method for evaluating corrosion activity in steel reinforcement within hardened concrete. It measures the electrical potential difference between embedded rebars and a reference electrode — typically a copper / copper sulfate (Cu/CuSO₄) cell. The test helps determine whether the reinforcement is actively corroding, passive, or at risk. A direct electrical connection is made to the rebar, and a grid of surface readings is recorded on moist concrete to ensure good conductivity. These readings are compared with standard probability charts provided in ASTM C876. The results allow engineers to locate corroded zones, plan preventive repairs, and avoid unnecessary concrete removal. Overall, it is a quick, reliable, and cost-effective tool for structural health assessment and durability maintenance of concrete structures.
Covermeter / Rebar Locator Test – Locating Reinforcement Without Damage
The Covermeter Test, also known as the Rebar Locator Test, is a widely used non-destructive testing (NDT) method for detecting the position, depth, and spacing of steel reinforcement in hardened concrete. It works by measuring the magnetic field disturbance created by embedded steel when scanned with an electromagnetic probe. The test accurately determines the cover thickness — the distance from the concrete surface to the reinforcement — which is critical for durability, fire safety, and code compliance. Modern covermeters can also estimate bar diameter and identify congestion or missing rebars. This method follows standards such as BS 1881-204 and helps engineers in repair planning, drilling, anchoring, and retrofitting without damaging the structure. Overall, the rebar locator test is fast, clean, and essential for structural assessment and quality control of reinforced concrete.
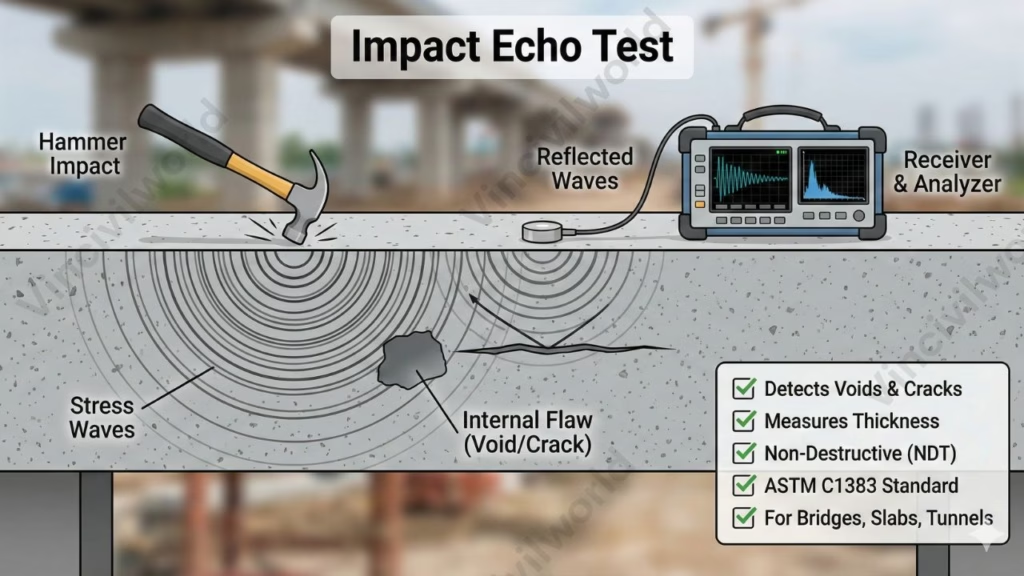
Impact Echo Test – Evaluating Internal Defects in Concrete
The Impact Echo Test is a reliable non-destructive testing (NDT) method used to detect internal flaws such as voids, cracks, delamination, and thickness variations in hardened concrete. It works by applying a short mechanical impact on the surface using a small hammer or impactor. This impact generates stress waves that travel through the concrete and reflect back from internal boundaries. A sensitive receiver records the returning signals and analyzes the wave frequencies to identify abnormalities. The method is guided by standards like ASTM C1383, making it suitable for bridges, slabs, tunnels, and precast elements. Engineers use this test to assess structural integrity, locate hidden defects, verify grouting, and ensure long-term durability—without drilling, cutting, or damaging the structure. Overall, the Impact Echo Test offers a fast and effective solution for concrete condition evaluation and maintenance planning.
Key Takeaways
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) evaluates hardened concrete’s strength and durability without causing damage, helping to detect hidden defects.
- Engineers use both non-destructive and destructive tests to ensure quality control and structural integrity during concrete assessments.
- Key advantages of NDT include quick results, safety, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for monitoring concrete structures over time.
- Various NDT techniques include the Rebound Hammer Test, Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity Test, and Impact Echo Test.
- These methods provide crucial insights into concrete quality, allowing for reliable repairs and maintenance planning.
Conclusion
Non Destructive testing of concrete plays a vital role in maintaining the long-term performance and safety of structures. NDT for hardened concrete enables engineers to assess strength, durability, reinforcement conditions, and internal defects without damaging the structure. With modern concrete NDT methods such as Rebound Hammer, Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity, Covermeter testing, Half-Cell Potential, and Impact Echo, engineers receive quick and reliable data on structural integrity. One of the major advantages of NDT is the ability to monitor existing buildings, identify deterioration early, and plan effective maintenance. By using advanced NDT techniques, the industry ensures cost efficiency, improved safety, and accurate decision-making throughout a structure’s life. Therefore, the advantages of NDT strongly support sustainable, safe, and high-quality construction management.










Thanks for sharing such informative content
Non-destructive testing plays important role in the inspection of the machines which results in greater productivity ensuring accuracy. Fast industrialization and the adoption of modern machinery are booming the non-destructive testing market globally.