Types of raft foundations are determined by the bearing capacity of the soil on which the structure is constructed, the structure’s applications, site conditions, design loads, and other factors. A continuous slab that completely encloses the intended structure and rests on the ground is known as a raft foundation. Raft foundation, also known as mat foundation, is a popular foundation system. A raft foundation is a type of shallow foundation. This article discusses the various types of raft foundations, as well as their advantages and disadvantages.
What is a raft foundation?
A raft foundation or mat foundation is a solid slab that is placed at a specific depth and covers the entire structure. Raft foundations are comprised of columns and shear walls that transfer loads to the ground. These foundations are appropriate for areas with a low bearing capacity, where individual footings struggle to traverse the loads. In addition to that, the raft foundation assists in the transfer of the structure’s entire load to a larger area.
When compared to other forms of foundations used in civil construction, they can reduce soil stress levels. In general, this stress distribution mechanism distinguishes raft foundations from other types of foundations.
Soil stress calculation
stress = total load coming on the structure + self-weight of raft/ Area of raft foundation
Consider a total load is 300 T and a foundation size
20 m x 10 m
Stress on the soil = 300/200 = 1.5 t/sqm
Same structure supported with 8 individual footing of
2 x 2 meter
total area = 8 x 4 = 32 sqm
Stress on soil = 300/32 = 9.375 t/sqm
In conclusion, for the same load we are getting stresses of 1.5 T/sqm for raft and 9.375 T/sqm for individual foundations.
In other words, we conclude that when the contact area of the raft is more, the load is distributed over a larger area and hence stresses coming on the soil are very less.
Types of Raft foundations – How to make a choice?
Raft foundations are preferred over other foundations when the following conditions are encountered.
- When the bearing capacity of the soil is very low, designing an individual footing and executing deep foundations like pile foundations turns out to be costly.
- When the bearing capacity of soil is less and stresses induced to the soil have to be reduced.
- The columns, shear walls etc are coming so close to each other and chances of individual footings overlapping each other.
- Any other type of foundation may cover more than 50% of the total ground area below the structure.
- When there is a possibility of unequal settlement.
- Preferred for complex equipment foundations.
- Used when the proposed structure has basements
Raft foundations are suitable for basement constructions where the foundation slabs can receive direct live loads according to the utility of the building. In sites where the soil conditions are very poor and access to large excavation machinery is restricted, raft foundations prove to be a better option as the excavations can be done with the help of light excavators.
Types of Raft Foundations
- SOLID SLAB RAFT FOUNDATION
- SLAB BEAM RAFT FOUNDATION
- PILED RAFT FOUNDATION
- CELLULAR RAFT FOUNDATION
- BALANCING OR FLOATING RAFT FOUNDATION
Solid slab types of raft foundations
In this type of raft foundation, the columns and walls are equally distanced and the load distribution is also equal. These types of raft foundations are designed as slabs with uniform thickness and are known as solid slab raft foundations. The reinforcement for these types of foundations comprises a bottom layer and a top.
There are four different types of Solid slabs
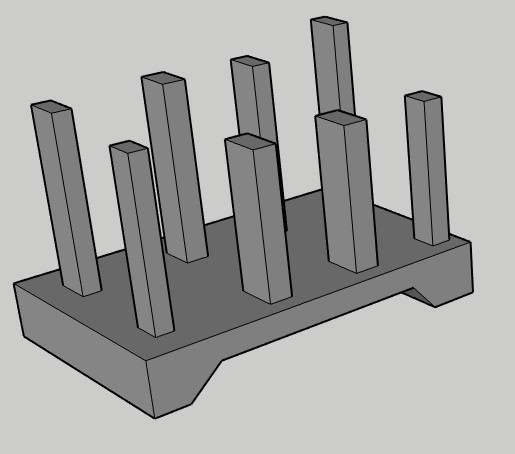
Wide toe types of raft foundation
The wide toe raft foundation is an economic foundation. A full-size solid slab mat foundation is not required for negotiating the design loads. For economizing the structure a heavily reinforced toe is provided on both sides as shown in the figure which can handle the loads.
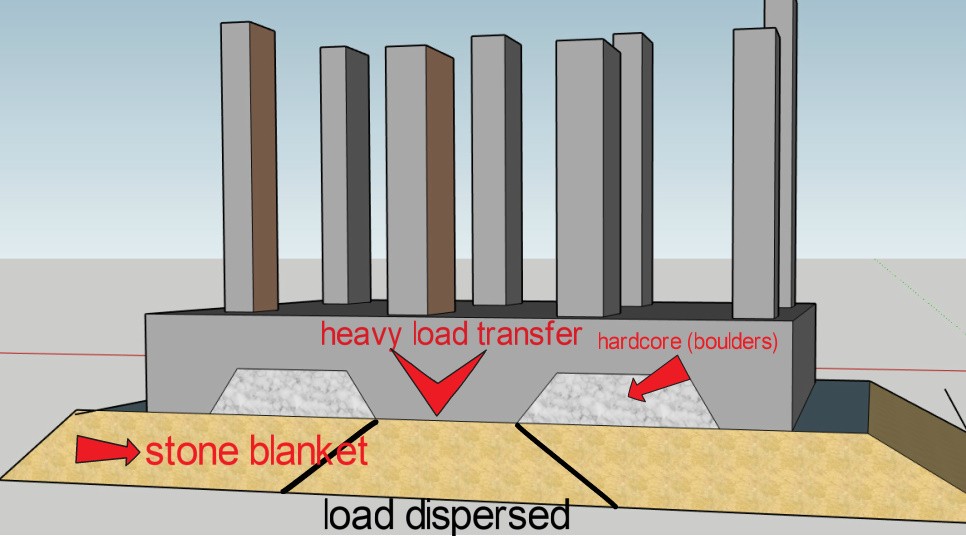
Blanket rafts
Blanket rafts are used when the surface may have unequal settlements or nonuniform strata. The surface is compacted and stone blankets are laid as shown in the figure. In this case, the stone blankets along with the raft shoes negotiate the load coming on the structure.
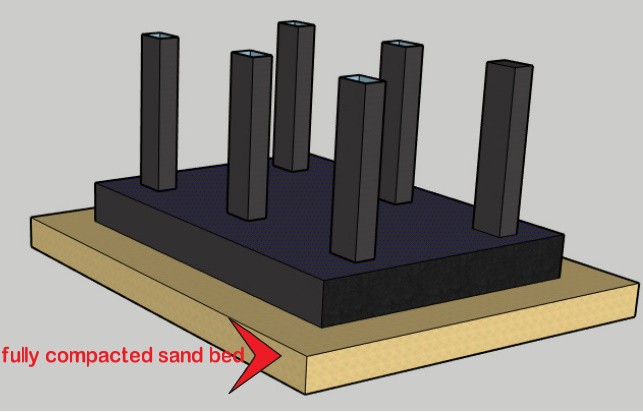
Slip plane rafts
This type of foundation bears a fully compacted sand bed beneath the raft. The sand bed size shall be kept a little bit larger than the raft size for the transfer of loads. The sides of the foundation can be filled with any compressible material.
Slab beam type raft foundations
When the loads are unequally distributed and the foundation is vulnerable to distortions. Beams included with the slabs act as stiffeners. The reinforcement of the raft constitutes two layers of meshes, one at the bottom and one at the top. The beams can provide extra stiffness and prevent distortions.
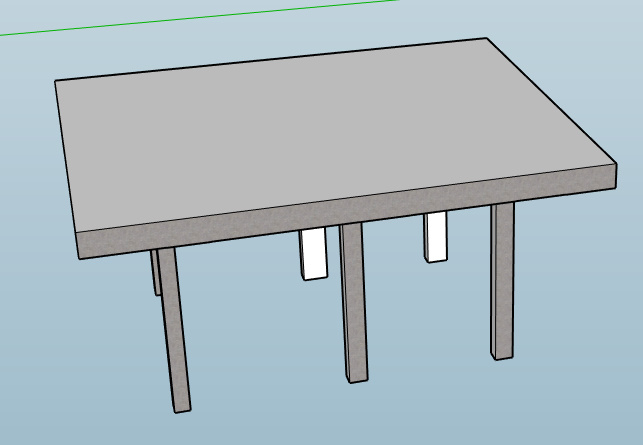
Piled raft foundation
Pile foundations are used to support the slab in case of piled raft foundations. Mostly used when the loads coming on the structure are extremely high, the soil bearing capacity is very low and the water table is very high. Mostly, piled raft foundations are well-suitable for high-rise buildings, heavy industrial structures like high-rise RCC chimneys, silos, and storage tanks which usually rest on single foundation elements. These types of foundations are not preferred for common residential applications due to their high costs. However, piled rafts eliminate the idea of designing a very heavy raft foundation or a very conservative pile foundation with larger depths. In place of that, they opt for a combination of an optimized raft foundation and pile foundation design capable of sharing the loads. The raft floats over the pile foundation.
Mostly used in structures like chimneys, silos, bunkers, overhead storage tanks etc where even a marginal settlement of soil may cause the structure to fail.
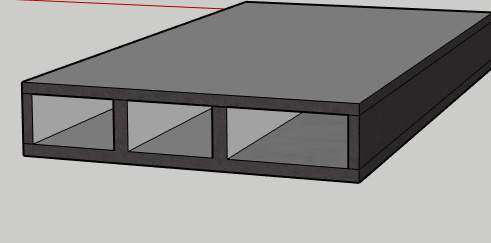
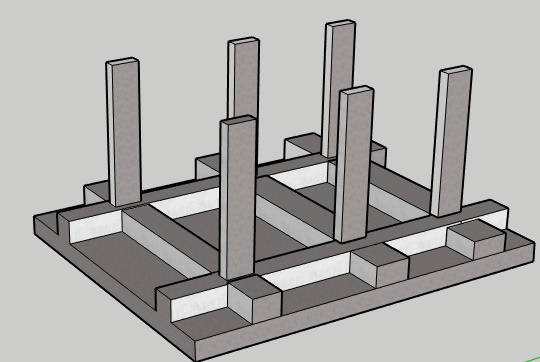
Cellular raft foundation
A cellular raft consists of an arrangement of two-way foundation beams with a solid slab resting on the ground below and a suspended slab at the top surface. Intermediates beams are provided between upper and lower slabs. The intermediate beam converts the total structure into an I Beam.
For covering the top slab precast soffits can be used. The top slab casting is done using precast soffits. or other forms of permanent formwork or sacrificial formwork or filled with lightweight infill blocks.
Mostly used in areas subjected to severe mining activity and having poor soil bearing capacities. Huge bending moments have to be resisted by the foundations. In those cases, cellular rafts are a preferred option. Cellular rafts are used when an increased bearing capacity is achieved in removing overburdens. Soil uplift pressure can be controlled by using cellular rafts.
Balancing raft or Floating Raft Foundation
Balancing rafts or floating foundations are used in areas where the bearing capacity of the soil is very poor and has to maintain the soil settlements within the acceptable range. The floating foundation works on the principle that the total weight of the soil along with water removed from the excavated area shall be equal to the weight of the proposed structure. However, this procedure requires extensive earthwork excavation. When the water table is exceptionally high, dewatering solutions such as well-point systems must be installed. Sheet piles will indeed be erected for unstable or potentially collapsing soils. Before beginning an excavation, temporary retaining walls and other preventative measures must be put in place to protect surrounding structures from soil-scoring damage. Some of these tasks must be completed concurrently with the excavation. This style of building is not cost-effective and requires minute technical supervision.
These foundation types are used to construct structures in densely populated areas while adopting all safety precautions to avoid damage to neighbouring structures. For structures with many levels of underground parking facilities, floating rafts are preferred. You can read our full article about floating rafts for more information.
Advantages of Raft Foundation – Videos
Raft foundations are a safe and economical solution compared with other shallow and deep foundation types.
- Preferred in areas with poor soil bearing capacity, uneven settlement, and the presence of mixed soil types. These foundations achieve load-bearing capacity through the distribution of stresses to a larger area.
- Used in dense urban areas where access to the sites is restricted and mobilisation of heavy machinery for foundation construction using other deep foundations like pile foundations is not possible. However, raft foundations can be executed using very light machinery due to their lesser heights.
- To restrict the settlement limits within the codal provisions the raft foundations provide a much-needed option for designers compared to other isolated foundations.
- The designers can opt for higher settlement values when compared with normal foundations while doing the design process. They can avoid unequal settlement
- Got Flexible design options and are customised as per the soil conditions and workability.
- The execution is easier than individual footings which in turn increases the speed of the project.
Disadvantages of Raft Foundation
- Raft foundations are not economical when the soil conditions are very poor.
- Complex raft foundations consume a huge quantity of concrete and steel and require precise professional/technical supervision and workmanship. This in turn makes the structure more expensive than any other alternative foundation.
- The soil below the foundation, mainly near the edges has to be preserved.
- Pile foundations are more economical than raft foundations when the soil conditions are very poor.


2 comments
Comments are closed.