Splitting tensile strength test is an essential method used to evaluate the tensile behavior of concrete. Since concrete is weak in tension, understanding the split tensile strength of concrete is critical for predicting cracking and durability. This test, also known as the indirect tensile strength test, applies compressive load along the diameter of a concrete cylinder to induce tensile stresses. Unlike direct tension tests, this method is simple, reliable, and widely adopted in laboratories. The tensile strength of concrete test provides valuable insight into concrete performance under shrinkage, temperature variation, and dynamic loading. Engineers commonly use the split cylinder test concrete to assess material quality and structural suitability. This article explains the test principle, procedure, standards, and practical applications in concrete engineering.
Table of contents
Significance of Splitting tensile strength test on concrete
The splitting tensile strength test is performed on hardened concrete to determine its tensile strength. Even marginal variations in the water–cement ratio, ingredient proportioning, or an increase in slump can impact the desired concrete strength. These changes directly affect the strength and stability of concrete structures. Therefore, accurate evaluation of concrete strength is essential.
Several tests are used to determine the strength of concrete at different stages. Quality tests on concrete must be conducted from the production stage to the hardened stage and even on completed structures. These tests play a crucial role in ensuring construction quality and structural reliability. This article focuses on the splitting tensile strength test of concrete to evaluate and derive the tensile strength of hardened concrete in a reliable and standardized manner.
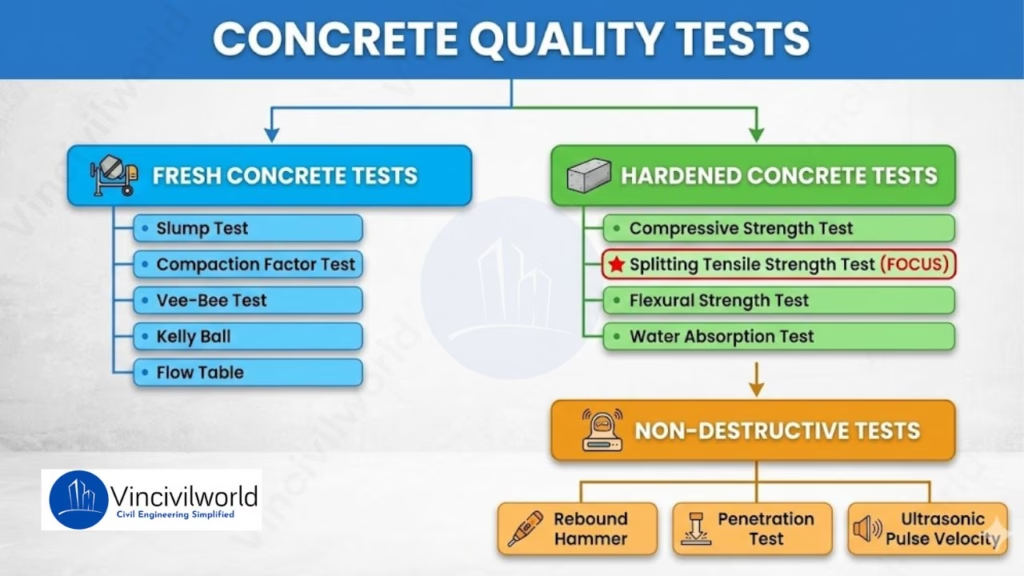
Quality tests on concrete
The Quality tests are done on different stages like production stage, hardened stage and Non destructive tests.
Quality tests on Fresh concrete
Quality tests on hardened concrete
- Compressive strength
- Splitting tensile strength test on concrete
- Flexural strength test
- Water absorption test
Non destructive tests on concrete
- Rebound hammer
- Penetration resistance test
- Ultrasonic pulse velocity test
In this article we deal with the Splitting tensile strength test of concrete.
Splitting tensile strength test – Definition and objectives
Since concrete is a brittle material, it is weak in tension and prone to cracking. Therefore, it is essential to conduct the splitting tensile strength test of concrete. This test determines the tensile strength of concrete indirectly by applying a compressive load on a cylindrical specimen, which causes it to split along its vertical diameter. Direct tensile testing of concrete is difficult to perform accurately, making this method more practical and reliable. To obtain consistent results, at least three specimens are tested and the average value is considered. The splitting tensile strength test helps engineers evaluate cracking resistance, material quality, and structural performance.
The main objectives are
- To determine the tensile strength of concrete and its resistance to cracking
- To provide information on the quality and suitability of sand and coarse aggregates
- To assess the uniform distribution of tensile stresses in concrete
- To study the behavior of concrete under indirect tensile loading conditions
Relevant code
- Indian Code (IS 5816) – Specifies procedure for splitting tensile strength test on concrete.
- American Code (ASTM C496) – Standard test method for split tensile strength of concrete cylinders.
- European Code (BS EN 12390-6) – Describes method for testing of hardened concrete.
The test procedures are fundamentally similar across IS, ASTM, and EN codes. Minor differences exist in specimen size, loading rate, and reporting format, but the testing principle remains the same.
Apparatus used
- Testing machine
- Plate or Supplementary Bearing bar
- Bearing strips
- Cylinder specimen
- Tamping rod
The testing machine should apply continuous load without shocks. So for this test, two bearing strips with 3.2 mm thick and 25 mm wide are used. The dimension of the cylindrical specimen is 150 mm in diameter and 300 mm in height.
Test procedure of Splitting tensile strength test
The splitting tensile strength test determines the tensile strength of hardened concrete using an indirect testing method. This standardized test evaluates cracking behavior and tensile resistance by applying compressive load along the diameter of a concrete specimen.
Procedure
- The first step is to prepare the concrete mix for making the cylindrical specimen.
- Grease the inside surface of the mould and Pour the mix into the mould as layers.
- Compact each layer using a tamping rod. Tap each layer 30 times.
- Uniformly stroke the concrete mix and remove the excess concrete.
- Then immerse the casted specimen in water for 24 hours at 27-degree celsius.
- After that remove the specimen from the mould and immerse it in freshwater.
- The splitting tensile strength of concrete should be conducted at 7, 28 days of curing.
- Before starting the test, take the specimen from the immersed water and wipe the water.
- Then note the dimension and weight of the specimen.
- Place plywood strip above and below the specimen
- After that place the specimen on the testing machine.
- Then gradually apply load at a rate of 0.7 to 1.4 MPa/min (1.2 to 2.4 MPa/min based on IS 5816 1999).
- Record the load at which the specimen breaks.
Calculation – Splitting tensile strength test
In the splitting tensile strength test of concrete, the tensile strength is calculated using the maximum applied load at failure. The formula is based on the applied load, diameter, and length of the cylindrical specimen. Accurate measurement ensures reliable evaluation of concrete tensile strength and cracking resistance.
Splitting tensile strength (T) = (2 × P) / (π × L × D)
Where:
P = maximum load at failure
L = length of the cylinder
D = diameter of the cylinder
The unit of tensile strength is N/mm. The splitting test is easy to perform and we can get uniform results. It is a simple, reliable and convenient method to determine the strength of concrete.
Key Takeaways
- The Splitting tensile strength test evaluates the tensile behavior of concrete, crucial for predicting cracking and durability.
- This test applies compressive load to a concrete cylinder, making it simple and reliable compared to direct tension tests.
- Accurate evaluation of concrete strength is vital, as variations can impact structural stability.
- The test involves preparing cylindrical specimens, curing them, and gradually applying load until failure occurs.
- Results help determine tensile strength, uniform stress distribution, and concrete’s suitability for various applications.
Conclusion
The splitting tensile strength test is an essential method for evaluating the tensile behavior of concrete. Since concrete performs poorly under tension, understanding the split tensile strength of concrete is critical for predicting cracking, durability, and long-term performance. The tensile strength of concrete test provides reliable insight into how concrete responds to indirect tensile stresses caused by shrinkage, temperature variation, and dynamic loading. Conducted using the split cylinder test concrete, this method is simple, repeatable, and widely accepted under IS, ASTM, and EN standards. As an indirect tensile strength test, it plays a key role in quality control, mix design assessment, and structural evaluation. Proper interpretation of test results helps engineers ensure safe, durable, and crack-resistant concrete structures in practical construction applications.





Split tensile test results should be added after curing for 7 and 28 days.